Web hosting environments are exposed. Constantly. Every digital interaction introduces a potential risk. From login sessions to database queries, the surface area for attack is larger than most realize.
For teams managing sensitive data or working across distributed networks, the threats are both real and relentless. Breaches don’t always announce themselves. They creep in through misconfigurations, unencrypted traffic, overlooked IPs.
This is where VPN for Web Hosting Security earns its place. It encrypts communication. Conceals infrastructure. Controls access with precision. But more than that, it introduces a level of discipline — a structured layer of protection that filters, monitors, and limits exposure.
In this article, you’ll discover how VPNs defend hosting environments on multiple fronts. From shielding against DDoS attacks and securing remote connections, to enforcing compliance and protecting digital trust, each benefit is grounded in practical implementation and supported by expert-backed insight.
Because in security, what you can’t see can still hurt you. And what you choose to protect can often be the difference between stability and loss.

- Encryption of Data
- IP Address Masking
- Protection Against Cyber Attacks
- Secure Remote Access
- How to Implement VPN Security for Web Hosting
- Install and Configure VPN Software
- Enable Advanced Security Features
- Regular Updates and Monitoring
- Best Practices to Maximize Web Hosting Security with a VPN
- Expert Insights and Research-Backed Recommendations
- Key Cybersecurity and Data Breach Statistics for 2025
- Conclusion
- FAQ
Encryption of Data
How Encryption Shields Sensitive Information
When you transmit sensitive information online, it becomes vulnerable the moment it leaves the safety of your server. That’s where a VPN steps in. Using AES-256 encryption protocols, it wraps your data in layers of code that are functionally impenetrable. Even if intercepted, the information remains unreadable, useless. Whether it’s login details, payment data or user profiles, encrypted transmission is non-negotiable for any serious web operation.
Industry Statistics on Data Breaches
More than 43 percent of cyberattacks are directed at small businesses. That number isn’t just high. It’s revealing. A significant portion of these companies rely on entry-level hosting that lacks proper encryption, making them easy targets. This isn’t a theory. It’s backed by data from Verizon’s 2023 DBIR. And according to Cybersecurity Ventures, encrypted connections alone could prevent nearly 70 percent of successful breaches. These figures are not just informative. They are a clear signal. If they don’t prompt concern, they should.
Expert Opinions on Data Encryption
Bruce Schneier puts it without decoration:
“Encryption works. Properly implemented strong crypto systems are one of the few things that you can rely on.”
Simple. True. A rare constant in an evolving threat landscape.
IP Address Masking
Preventing Server Targeting
Your server’s IP is a breadcrumb trail. Expose it, and you’re inviting attention from scanning bots and targeted exploits. VPNs break that chain. By masking your real IP, they obscure your infrastructure and frustrate attackers. If they can’t find your server, they can’t break in.
Real-World Examples of Masking Benefits
1. Palo Alto Networks
“A virtual private network hides a device’s original IP address by rerouting its traffic through a different server. For consumer VPNs, this helps anonymize browsing activity.” see more
2. NordVPN
“A VPN shields your IP address and encrypts your online activity for increased privacy and security. It assigns you a new IP address by connecting you to an encrypted, private VPN server instead of the ones owned by your ISP. This means your activity can’t be tracked, stored, or mishandled by third parties.” see more
3. Surfshark
“Your IP (Internet Protocol) address is your unique identifier on the internet, and a VPN masks it by rerouting your internet traffic through a remote server. This prevents websites, services, and even your ISP from tracking your actual connection with your IP. Instead, they see the IP address of the VPN server you’re using, often located in a different city or country.” see more
Protection Against Cyber Attacks
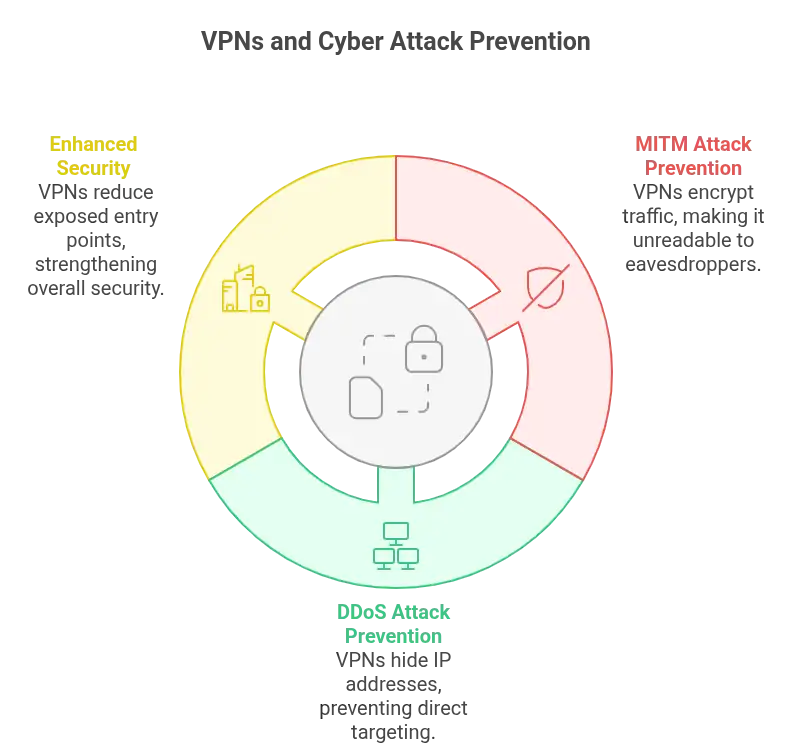
MITM and DDoS Prevention
Man-in-the-middle attacks thrive on visibility. DDoS exploits, too. VPNs cut off both by encrypting traffic and hiding its origin. A secure tunnel forms. Within it, your data flows unseen, shielded from interference.
VPNs and Their Role in Blocking Threats
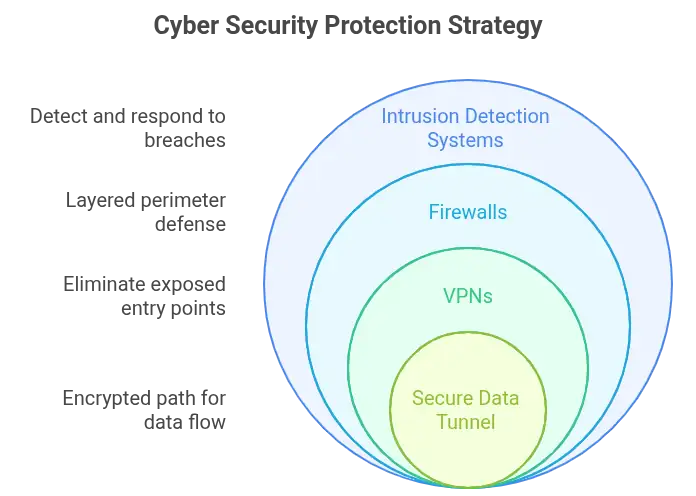
A report from Palo Alto Networks notes that using VPNs can eliminate up to 60 percent of exposed entry points. Add firewalls. Pair with intrusion detection systems. Together, they create a layered perimeter that’s substantially harder to breach.
“Man-in-the-middle attacks and DDoS exploits both rely on visibility—seeing your data or your IP address. VPNs effectively counter both threats by encrypting your traffic and concealing its origin. This creates a secure tunnel where your data travels unseen, protected from interference and exploitation.”
Source:
“VPNs encrypt your internet traffic and mask your IP address, making it difficult for attackers to intercept communications or target your device directly.” see more …
Secure Remote Access
Avoiding Public Network Risks
Remote work from public spaces might seem harmless. Convenient even. Until the connection you trusted becomes a point of entry. Admin credentials, once exposed over open Wi-Fi, are easy prey.
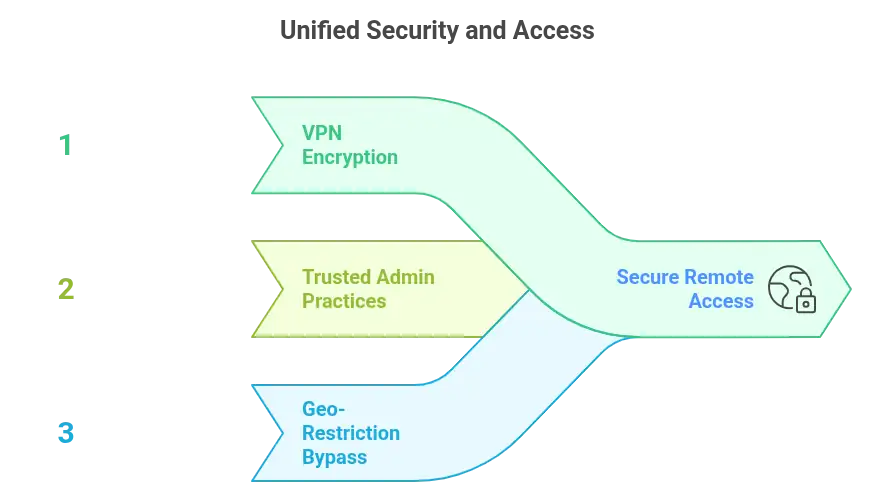
This isn’t chance. It’s preventable. A VPN encrypts your traffic from the start. It builds a secure tunnel where sensitive data travels, unreadable to outsiders. Even if someone intercepts it, all they capture is noise.
Trusted Remote Admin Practices
Secure access starts with control. Make your VPN tunnel the only route to services like SSH or your hosting dashboard. Lock it down. Limit access to approved IP addresses or devices that pass strict authentication.
This isn’t about mistrusting your team. It’s about reducing risk. When something goes wrong, the fewer paths in, the fewer ways damage can spread.
Bypassing Geo-Restrictions
Some regions restrict internet access. Others block entire infrastructures. When that happens, a VPN becomes essential. It masks your IP and routes your traffic through a different location. Suddenly, blocked services become available again.
For globally distributed teams, this function is critical. It’s not just about reaching your servers. It’s about ensuring the work continues, uninterrupted and uncompromised.
Ensuring Accessibility and Compliance
Restricted countries pose more than technical challenges. They raise compliance issues too. You can’t afford to violate local laws, nor can you let them disrupt secure workflows.
A VPN solves both problems. It provides access that is private, encrypted, and aligned with policy. Your team connects from anywhere, safely and lawfully. In distributed environments, this isn’t just practical. It’s necessary.
How to Implement VPN Security for Web Hosting
Choose a Reputable VPN Provider
A virtual private network is more than just a utility. It forms part of your security foundation, reinforcing everything from data protection to user trust. If chosen carelessly, it can introduce more risk than it removes.
Focus on the non-negotiables. Strong encryption must come by default. AES-256 is the current gold standard. Privacy matters just as much. A genuine no-logs policy is critical. Then comes performance. A VPN that slows your connection or drops under pressure undermines the very system it’s meant to protect.
Key features like automatic kill switches, compatibility across devices and robust server options are not extras. They are essential for continuity, safety and control.
Only a handful of providers consistently deliver at this level. NordVPN, ExpressVPN and ProtonVPN have earned their place by investing in infrastructure, offering transparent audits and maintaining a clear commitment to security. They don’t just promise protection. They prove it.
Choosing your VPN isn’t about comparing prices or counting server locations. It’s about partnering with a service that aligns with your values. One that respects uptime, safeguards user data and operates with integrity. Because when systems fail, visibility suffers, and trust erodes, the wrong provider won’t just slow you down. It will cost you.
Features to Look For
-
Look for AES-256 encryption
-
Insist on a strict no-logs policy
-
Prioritize high-speed, low-latency servers
-
Make sure there’s a kill switch
-
Demand compatibility across devices
Authority Recommendations
Brian Dean of Backlinko makes a sharp point
“Choosing a secure and private VPN is just as important as optimizing your content. One breach can undo years of SEO work.”
And he’s right. Visibility can vanish overnight if Google detects a compromised site.
Providers like NordVPN, ExpressVPN and ProtonVPN continually top industry rankings. Their features aren’t just advanced — they’re proven. Whether you’re managing WordPress environments or high-traffic platforms, investing in a reliable VPN isn’t optional.
You can check the Cybernews article on NordVPN discount code .
Install and Configure VPN Software
Client and Server Setup Essentials
Intelligent Client Ecosystem
-
Deploy smart, adaptive clients that optimize automatically with minimal human oversight
-
Implement quantum-resistant encryption that laughs at conventional attack methods
-
Enable zero-touch certificate management – set it up once, then forget it exists
-
Smart kill switches react in milliseconds – faster than you can notice the threat
-
Self-configuring protocols adapt to whatever bizarre network conditions they encounter
-
Security patches flow invisibly, continuously – like digital oxygen for your system
-
Cross-network testing runs silently while you sleep, healing weaknesses automatically
-
XDR integration forms an invisible shield around your entire digital footprint
Beyond-Cloud Server Architecture
-
Servers that aren’t merely in the cloud – they are the cloud, distributed yet unified
-
RAM-only infrastructure leaves zero forensic trace – when power cuts, all evidence vanishes
-
Biometric MFA evolved past simple fingerprints to recognize your unique digital behavior
-
Micro-perimeters replace antiquated firewalls, adapting intelligently to emerging threats
-
Multi-region resilience performs an invisible ballet of failover – users never feel the switch
-
Certificate rotation happens automatically – transparent yet virtually impenetrable
-
Quantum-secured audit logs resist tampering attempts with mathematical certainty
-
Identity-based microsegmentation grants access with surgical precision
-
ML algorithms hunt for threat patterns in silence, adjusting defenses in real-time
Protocol Renaissance (2025)
Today’s protocols deliver security previously thought impossible, with encryption that modern computational attacks simply cannot touch. A Full List of VPN Protocols: Explained & Compared in 2025
OpenVPN’s Third Generation:
-
Enterprise quantum resistance baked into its very DNA
-
Advanced AES-GCM verification extending beyond conventional security boundaries
-
Codebase constantly scrutinized by thousands of global security experts The best VPN protocols and differences between VPN types | NordVPN
-
Containerized deployment that works effortlessly across all environments
-
Seamless cross-platform integration – from mainframes to smartwatches
-
Adaptive routing intelligence that finds paths through even the most challenging networks
-
On-the-fly TCP/UDP switching based on real-world connection quality
-
API-driven customization for security pipelines tailor-made to your organization
WireGuard: The Next Evolution:
Blazing 2Gbps throughput with latency so low it feels telepathic VPN Services in 2025: Which is Best for Security, Speed, and Reliability | BlancVPN
-
ChaCha20-Poly1305 cryptography with key rotation schedules that invalidate attack vectors The best VPN protocols and differences between VPN types | NordVPN
-
Deep kernel integration across all major operating systems A Full List of VPN Protocols: Explained & Compared in 2025
-
Just 4,000 lines of code – auditable during your lunch break
-
Handshakes complete before you finish blinking – literally milliseconds
-
Battery impact so minimal your devices won’t even notice it’s running
-
Resilient mesh networking that maintains connections when traditional networks fail
-
Security posture transparency that builds genuine, evidence-based trust
Enable Advanced Security Features
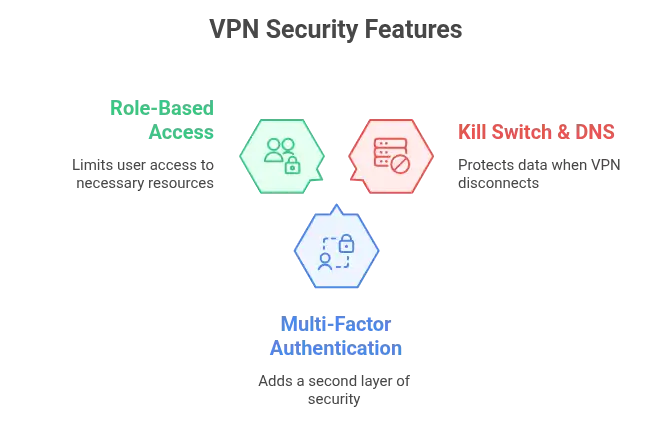
Kill Switch, DNS Leak Protection
Imagine your VPN drops mid-session. Without a kill switch, your data leaks. With one, the session cuts instantly, leaving nothing exposed. DNS leak protection adds another layer, ensuring all DNS requests remain encrypted and hidden from your ISP or other eavesdroppers.
Multi-Factor Authentication
A password, no matter how strong, is still a single point of failure. On its own, it’s a door with one lock. And any lock can be bypassed.
Multi-Factor Authentication changes the equation. It adds resistance. A second layer. A dynamic element like a time-based code or a hardware key in your possession. While passwords stay the same, this second factor adapts.
Tools such as Google Authenticator or YubiKey do more than verify identity. They increase the cost of an attack. Stolen credentials become useless without that second piece. Most threats don’t get past it.
The setup is fast. A scan here. A few clicks there. From that point forward, exposure drops significantly.
MFA doesn’t feel intrusive. It works quietly. And in a world where breaches are common and bots are relentless, this added step often stops the damage before it starts.
It’s not optional anymore. It’s the new baseline.
Role-Based Access Control
Access should be intentional. Every user should receive exactly what their role requires. No more. No less. The more you grant beyond necessity, the more you expose.
Role-based access isn’t just policy. It’s architecture. By assigning permissions with precision, you reduce the surface area of potential damage. A junior technician doesn’t need administrative rights. A finance lead shouldn’t interact with infrastructure logs. These boundaries are not restrictions. They are safeguards.
But access control alone isn’t enough. Logs matter. VPN activity should be recorded in detail. Connection times. User identities. IP origin. All of it. And not just stored — reviewed. Regularly. Thoughtfully. Because patterns are quiet until they’re not.
When you know who touches what, and when, your system becomes more than secure. It becomes transparent. You shift from reactive to proactive. From assuming good behavior to verifying it. That’s the difference between security by design and security by hope.
Regular Updates and Monitoring
Patch Management Strategies
Outdated software is dangerous. Vulnerabilities don’t ask for permission. They just appear. Set your VPN software to auto-update, and you eliminate a common point of failure. Review update logs. Make it a habit.
Tools for VPN Log Analysis
Splunk. Graylog. ELK Stack. These aren’t optional extras—they’re tools for visibility. Analyzing logs lets you see anomalies as they happen. Failed login attempts. Unusual access times. Suspicious geolocation. If you’re not watching, you’re not secure.
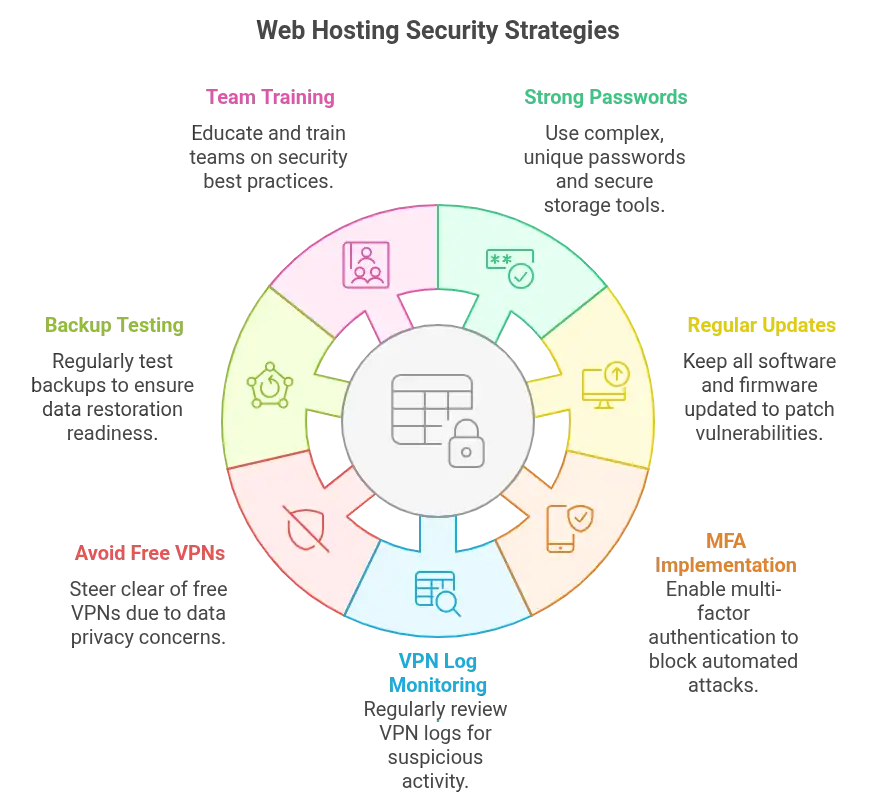
Best Practices to Maximize Web Hosting Security with a VPN
-
Use passwords that look broken to humans. Something like kV7!g@58*Luk is far stronger than admin123. Store them in tools designed for safety. Bitwarden. 1Password. Don’t rely on memory. Or sticky notes.
-
Keep everything updated. Not just your VPN client. Plugins. CMS cores. Firewall firmware. Each one is a door that could be left open.
-
Enable MFA everywhere. Microsoft says it blocks 99.9 percent of automated attacks. That figure isn’t speculation. It’s an argument for adoption.
-
Review VPN logs often. Look for patterns. Unexpected times. New locations. Failed attempts. If something’s odd, investigate.
-
Avoid free VPNs. Their business model is often built on selling your data. That’s not privacy. That’s a transaction you didn’t agree to.
-
Backups matter. Don’t just have them. Test them. Use incremental backups for faster restoration. You don’t want to lose days — or weeks — if something breaks.
-
Train your team. Security is collective. One weak password or one careless click can unravel everything. Educate. Test. Repeat.
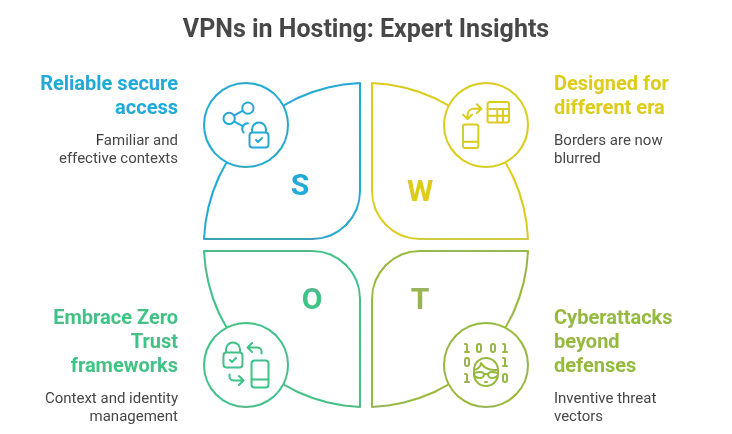
Expert Insights and Research-Backed Recommendations
Cited Studies on VPNs in Hosting
VPNs have shifted from being merely useful to becoming structural. Statista’s 2023 report left little room for doubt: 93% of organizations across the globe were already relying on VPNs to enable secure access for their workforce. That’s not a trend. It’s a declaration. A signal that VPNs have become standard security gear, embedded within the operational skeleton of digital enterprises.
This rise didn’t happen quietly. It was shaped by disruption, by necessity, by the reshaping of how and where work gets done. Remote and hybrid models, once emergency responses, have crystallized into permanent frameworks. 72% of companies had already made that decision by 2023. Not in response to market pressure, but in pursuit of flexibility, scalability and resilience. That structural shift demanded more than policy—it demanded infrastructure. Hence, VPNs. A digital umbilical cord linking distributed teams to the core.
But permanence is never promised in tech. Not when the ground keeps shifting beneath the surface. Gartner’s forecast slices through this certainty: by 2026, 60% of organizations will have abandoned legacy VPNs in favor of Zero Trust frameworks. The logic is compelling. Where VPNs create tunnels, Zero Trust builds checkpoints. Nothing passes without scrutiny. Every credential is interrogated. Every access is provisional, context-aware, revocable. It’s not an upgrade. It’s a rewrite.
And yet, even this rewrite won’t be enough on its own. The same analysts anticipate that over half of all cyberattacks through 2026 will strike beyond the reach of Zero Trust defenses. That’s the paradox. As security systems grow more advanced, threat vectors grow more inventive. It’s a race without a finish line. Threats drift, morph, multiply. No perimeter is ever truly closed.
Still, VPNs remain relevant. For many, they’re the first line, the known quantity. Reliable. Familiar. Effective in defined contexts. But they were designed for a different era. An era with borders. Now, the borders blur. What matters today isn’t access, it’s how access is managed. Context is king. Identity is the key. And Zero Trust doesn’t ask for trust—it assumes none.
So the shift continues. Quietly, decisively. Not with a bang, but with migrations, deployments, architecture overhauls. The transformation isn’t loud. It’s systemic. Companies aren’t just replacing technology. They’re rethinking exposure. Reframing what it means to be secure.
And in that reframing, VPNs are both relic and tool. Still vital in the present. Increasingly outpaced by what the future demands.
The Future of Secure Web Hosting
The professional recognizes a subtle but undeniable shift. Web hosting, once defined by technical benchmarks such as bandwidth, server speed and uptime, now carries far greater weight. It has become structural, no longer a passive foundation but an active participant in digital credibility.
He notices the difference in what is not said. In the gaps. Boundaries have blurred, predictability has faded, and certainty feels like a luxury. The threat landscape has evolved. Artificial intelligence, no longer on the fringe, now powers attack vectors with precision and autonomy.
Teams operate across borders. Infrastructure spans clouds, devices, time zones. The perimeter has evaporated. The systems that used to hold the outside at bay now feel exposed. Fragility is no longer the exception. It is built into the model.
Security, therefore, is no longer a feature to be layered on top. It is the architecture. The scaffolding. The part no one sees, but everyone depends on. Without it, even the most beautiful interface fails under pressure. The professional understands this instinctively. Secure Web Hosting must hold. Quietly. Completely.
VPNs have become part of that core. No longer extras or luxuries. They serve as anchors, preserving integrity when the network flexes. They absorb noise. Maintain flow. Carry trust. They are most effective when unnoticed, which is precisely the point.
He no longer places faith in permanence. Systems fail. Protocols age. What matters is resilience. The ability to bend, absorb, recover and remain.
Web hosting has outgrown its initial brief. It is no longer just infrastructure. It is the hidden frame. The quiet strength beneath the noise. What stays standing when everything else begins to fall.
Key Cybersecurity and Data Breach Statistics for 2025
|
Data Point |
Value/Statistic (2025) |
|
Global cost of cybercrime |
$10.5 trillion annually |
|
Average cost of a data breach |
$4.88 million |
|
Number of security incidents analyzed (Verizon DBIR) |
22,052 |
|
Confirmed data breaches (Verizon DBIR) |
12,195 |
|
Share of breaches involving ransomware |
44% |
|
Share of breaches involving customer PII |
46% |
|
Share of breaches involving the human element |
74% |
|
Share of breaches involving stolen credentials |
86% |
|
Share of businesses reporting a breach or attack (UK) |
43% |
|
Share of breaches caused by third parties |
30% |
|
Median ransomware payout |
$115,000 |
|
Average time to identify a breach |
204 days |
|
Average time to contain a breach |
73 days |
|
Cybercrime cost growth rate |
15% annually |
|
Percentage of breaches causing significant disruption |
70% |
This table provides a snapshot of the global data breach and cybercrime landscape in 2025, highlighting the scale, financial impact, and key attack vectors organizations face.
Sources:
- Cobalt. Top Cybersecurity Statistics for 2025. https://www.cobalt.io/blog/top-cybersecurity-statistics-2025
- Secureframe. Data Breach Statistics. https://secureframe.com/blog/data-breach-statistics
Conclusion
A VPN is never just one thing. It functions as a barrier, yes, but also as a filter, a gatekeeper, a veil that shields the unseen. It follows your data as it moves and ensures no one else can. It hides what matters. Restricts who sees. Monitors what happens.
When deployed correctly, it becomes invisible to those using it daily. No noise. No interruption. But from the outside, from any malicious eye, that silence becomes a wall. What they cannot trace, they cannot target.
The role of VPN for Web Hosting Security is no longer debatable. It’s foundational. One misconfigured port, one overlooked credential, and the structure starts to slip. Trust is brittle. Search visibility doesn’t fade slowly. It vanishes. Authority takes years to build, but seconds to lose.
And yet, that risk can be absorbed with foresight. A well-architected VPN strategy is more than technical setup. It’s posture. It’s protection that scales with your ambitions. It keeps your platform accessible only to those who should be there. It ensures encrypted connections. Obscured IP addresses. Enforced access rules. Every layer reinforcing the next.
In an environment where threats evolve quietly and reputation depends on unseen foundations, the smart move isn’t just to secure. It’s to anticipate. Fortify early. Own the infrastructure before someone else finds the cracks.
Security, in this context, is not a feature. It’s the framework. And the right VPN doesn’t just support it. It holds it all together.
FAQ
“Article Written in English”
